A popular bumper sticker in the United States – typically seen on large vehicles, with giant wheels and vibrating chrome muffler pipes – reads: “My carbon footprint is bigger than yours.” This appears as a banner for the culture of extravagant indulgence. And wherever consumption is encouraged and admired, waste follows.
The world’s rich cultures are all wasteful, and not just because of excessive fossil fuel use. Even our modern electronic devices represent a massive waste stream. Last year, electronic waste reached an all-time record of 65 million tonnes.
Planned Obsolescence

Even modern LED light bulbs, for example, do not last as long as incandescent bulbs made a century ago. One carbon filament light bulb, at a fire station in Livermore, California, is still burning continuously after 120 years. Building things that last, and consuming modestly, used to be common human values. But that all changed with the advent of contemporary business models and modern marketing.
In 1924, three companies – Dutch Philips, German Osram, and US General Electric – formed a cartel, Phoebus, to shorten the life of light bulbs. Making light bulbs that could last 100 years limited their sales growth. They agreed on a thousand-hour standard, about three or four months of normal use, the historic beginning of planned obsolescence.
During World War I, the U.S. Treasury Department launched a frugality campaign to save resources for the war effort. Merchants, however, opposed the initiative. According to Giles Slade in Made to Break, US stores displayed signs such as, “Beware of Thrift,” and “Business as Usual.” New York retailers formed the “National Prosperity Committee,” with slogans like, “Full Speed Ahead!” and “Clear the Track for Prosperity!”
During the global economic depression in 1932, New York manufacturers circulated a pamphlet: “Ending the Depression through Planned Obsolescence,” the first known printed use of this phrase. An article in Printer’s Ink journal warned that the idea of durability was “outmoded,” claiming that, “If merchandise does not wear out faster, factories will be idle, people unemployed.” Paul Mazur, a partner at Lehman Brothers, declared that obsolescence, designing products to fail or wear out, was the “new god” of business philosophy.
In 1950s America, advertising firms learned that they could sell products not based on function, quality, or durability, but on novelty. Products were sold as “new,” “modern,” and “innovative,” whether or not the “innovations” offered any genuine value. The throwaway fashion industry was born on the notion that clothing “styles” allegedly changed every year, and that to appear “modern,” one must repeatedly buy new clothing. Ad agencies convinced popular journals to publish fashion sections to inform, or manipulate, the public regarding the latest styles.
Thus, the idea of well-made, durable products died away in rich nations, replaced by products that break, wear out, become obsolete, or go out of fashion. This trend has now seized the modern electronics industry.
E-waste and the cost of high tech

Since the 1980s, computers and electronic devices have made lives in rich countries more convenient and entertaining. Some observers expected that modern electronics would also make society more “efficient,” that computers would save paper and other resources. Those hopes, however, encountered what is known in economics as the “rebound effect“: Efficiency often leads to more resource use, not less. Human enterprise now uses six times more paper than we used at the dawn of the computer age, six times more lithium, five times more cobalt, more iron, copper, and more rare earth metals.
Mining for these minerals tends to be ecologically destructive and exploitive of human labourers. Due to increasing demand and low rates of electronics recycling, mining companies are now proposing strip mines on the ocean floor, a practice that ocean biologists say would permanently damage unique and biodiverse ocean ecosystems.
As computer chips got smaller, more powerful, and more energy efficient, the material and energy intensity of those chips increased exponentially. Since our computers require so little energy to operate, we may believe they are “efficient,” but we are measuring the wrong metric. To understand the high cost of high tech, we must consider the embodied energy built into our devices, our telecom infrastructure, server networks, and data centres. We also have to consider the sheer growth of consumption and the acceleration of waste.
According to Statisa, about 4 million cell phones are sold every day, over 1.5 billion per year. About 250 million computers are sold each year. The average lifetime of these devices is now about two and a half years. Manufacturers design in obsolescence, changing critical parts and marketing more fashionable, “improved” devices. We may marvel at social media and connectivity, but this level of consumption leaves behind a massive, toxic, and destructive waste stream.

Apple Corporation has become notorious for designing smartphones, tablets, and laptops that are difficult to repair or upgrade. These policies are not an accident or a necessity of technological advance. They are marketing decisions, designed specifically, like the three-month light bulb, to sell more products.
Between June 29, 2007 and November 3, 2017, Apple introduced 14 new iPhone models, one every 37 weeks. The company stopped supporting the first generation phones within three years, and continues to make previous phones obsolete and unsupported.
According to Jason Koebler at Motherboard, “Apple is trying to kill legislation that would make it easier for normal people to fix iPhones.” Apple designs products with proprietary parts that cannot be easily repaired and the company has actively lobbied against right-to-repair legislation in the US. According to a Repair.org study, both Apple and Sony have blocked environmental electronics standards that would support repair, upgrade, and recycling.
However, Apple Corporation is not alone. According to a 2017 Greenpeace report, other consumer electronics companies are lagging far behind. Although Apple has made progress in the use of renewable energy they are “moving in the wrong direction,” along with Microsoft and Samsung, by shortening the useful life of devices. Samsung, Amazon, Oppo, Vivo, and Xiaomi receive failing grades in every category, using toxic chemicals and dirty energy, making short-lived products that are difficult to recycle, and hiding the data about their practices. On the other hand, HP, Dell, and Fairphone are leaders in producing products that are repairable and upgradable.
Electronic waste has now reached over 65 million tonnes per year. Computers, screens, and small hand devices comprise about 22% of that waste, 14 million tonnes annually. According to a 2014 UN Report, Europe produced the highest per-capita electronic waste, over 15 kilograms per person every year. Asia generated the most e-waste, 16 million metric tonnes, followed by the Americas, 11.7 million tonnes per year. Since 2014 those volumes have increase by about 50%.
System Change
As with most of our ecological challenges, there are solutions, but the response requires more than marginal change. According to Deishin Lee, at MIT’s Sloan School of Management, “most waste is generated on purpose,” built into modern business models. Lee criticizes “output-oriented,” production systems that only consider the product. “Every output-oriented process,” she writes, “is designed to produce waste.” We can overcome this by shifting to input-oriented production, considering the value of all resources, how to conserve, and how to use resources effectively, with a minimum of waste.

Economist Tim Cooper, at Nottingham Trent University believes that a transformation away from planned obsolescence will require a “radical, systemic change.” In his book, “Longer Lasting Products,” Cooper suggests the change could be accomplish with economic policies to encourage minimum standards of durability, repairability, and upgradeability.
Quality goods, robust repair-and-servicing, and secondhand markets would result in more jobs and more economic activity for a given amount of resources. Cooper calculates that when consumers spend less on throwaway products, they will spend more for other services and investments.
In “Culture of Waste,” Julian Cribb, a fellow of the Australian Academy of Technological Sciences and Engineering, describes how we could reverse the trends toward food waste with government regulation to limit wasteful practices, full-cost pricing and taxing, subsidies for good stewardship production, and with education. The 2017, Greenpeace Report, advocates similar actions to create closed loop, circular production, beginning at the design stage, with all companies required to design recyclable parts, easy repair, and a take-back program for all products.
Growth swamps efficiency
Everything we build requires energy. Wasteful practices waste energy. Although we are witnessing an unprecedented effort to develop renewable energy, we are failing to keep pace with growth in demand. Unless we address the growth of human numbers and human enterprise, we are destined for the natural results of ecological overshoot. We also need to phase out fossil fuels and redouble efforts to build renewable energy infrastructure.
The following chart – prepared by Canadian energy engineer David Hughes, using data from the 2019 BP Energy Review – shows the annual growth in renewable energy compared to the annual growth in electricity demand. A great deal of this demand is due to wasteful manufacturing and sales practices. Two-thirds of the growth is met with fossil fuels. Furthermore, this only accounts for electricity. 83% of the world’s energy consumption is non-electric.
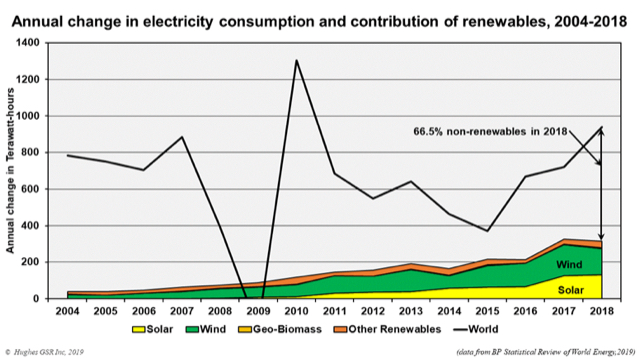
The only year that renewable energy growth exceeded demand growth occurred in 2009 during an economic recession. This chart reveals two critical pieces of our waste and energy challenge: (1) Renewable energy growth is not keeping pace with total energy demand, and (2) The way to turn this around is to end the expectation of endless economic growth. Some companies, such as Fairphone and Patagonia, have business models that account for slowing growth.
The idea that we should keep businesses growing by creating waste is no longer valid – and never was. We can employ more people by building quality products and repairing them. To reverse the trend of wasteful production, biodiversity collapse, carbon emissions that cause global heating, and general ecological overshoot, humanity has to embrace modest consumption and put an end to the era of extravagant indulgence.
References and Links
“E-waste World Map Reveals National Volumes, International Flows,” StEP Initiative, 2013, Quoted in Greenpeace E-Waste report, 2016.
E-waste: The Escalation of a Global Crisis, TCO certified
“Made to Break: Technology and Obsolescence in America,” Giles Slade, Harvard University Press, 2007; and excerpts at Google Books.
“A Culture of Waste,” Julian Cribb, Ecology Today, 2012.
Guide to Greener Electronics 2017, Greenpeace Reports, October 17, 2017
“Overcoming the culture of waste” Deishin Lee, MIT, Sloan School of Management, 2017.
Power-hungry gadgets endanger energy efficiency gains, review of The International Energy Association analysis, John Timmer, 2009, ARS Technica.
The Global E-waste Monitor, 2014: UN University, 2014.
“Electronic Waste (E-Waste): How Big of a Problem is it?” Rubicon, 2018
Facts and Figures on E-Waste and Recycling, Electronics Takeback Coalition, 2014
“The monster footprint of digital technology,” Kris de Decker, Low-Tech Magazine,
“Electronics Standards Are In Need of Repair,” Mark Schaffer, Repair.org, August 2017.
“Apple is against your-right to repair i-Phones New York state records confirm,” Jason Koebler, Motherboard, 2017.
“Longer Lasting Products: Alternatives to the Throwaway Society,” Tim Cooper, Gower Books, 2010.
Culture and Waste: The Creation and Destruction of Value, Edited by Gay Hawkins and Stephen Muecke, Rowman & Littlefield, 2002.
“The L.E.D. Quandary: Why There’s No Such Thing as ‘Built to Last’,” J. B. MacKinnon, New Yorker, 2016.
“Patagonia’s Anti-growth Strategy,” J.B. MacKinnon, New Yorker, 2015.
